Frequency and Relative Prevalence of Calcium Blips and Puffs in a Model of Small IP3R Clusters
Abstract
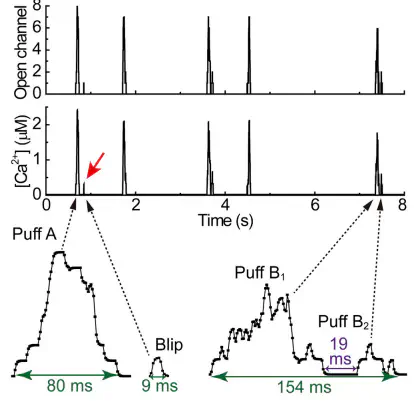
In this work, we model the local calcium release from clusters with a few inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) channels, focusing on the stochastic process in which an open channel either triggers other channels to open (as a puff) or fails to cause any channel to open (as a blip). We show that there are linear relations for the interevent interval (including blips and puffs) and the first event latency against the inverse cluster size. However, nonlinearity is found for the interpuff interval and the first puff latency against the inverse cluster size. Furthermore, the simulations indicate that the blip fraction among all release events and the blip frequency are increasing with larger basal [Ca(2+)], with blips in turn giving a growing contribution to basal [Ca(2+)]. This result suggests that blips are not just lapses to trigger puffs, but they may also possess a biological function to contribute to the initiation of calcium waves by a preceding increase of basal [Ca(2+)] in cells that have small IP3R clusters.