Abstract
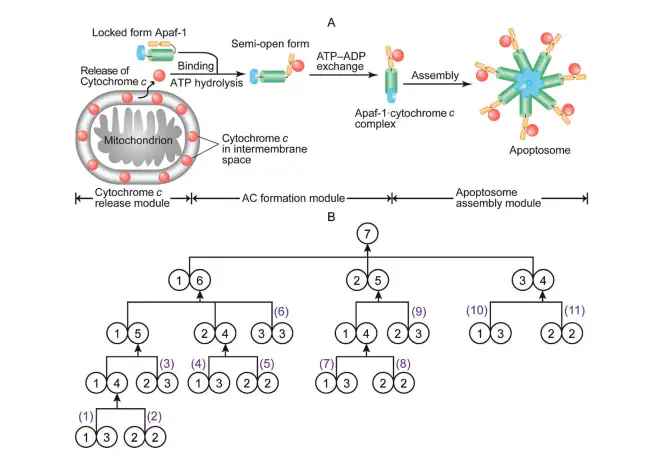
The formation of a heptameric apoptosome is a crucial event in the intrinsic cell death pathway. Considerable progress has been made towards unraveling the constituents and the structure of the apoptosome as well as the mechanism of apoptosome-mediated caspase-9 activation. However, a significant gap remains in the understanding of this process, i.e., how seven Apaf-1·cytochrome c complexes stepwisely assemble into an apoptosome. Here, we construct a biophysical model that incorporates current biochemical knowledge about the formation of apoptosome. We propose 11 elementary routes and enumerate all 2047 possible assembly pathways from the Apaf-1·cytochrome c complex to the heptameric apoptosome. By combining mathematical analysis and numerical simulation, we find that two elementary routes are the most favorable biochemical reaction routes and there are 52 optimal assembly pathways which are economical and relatively fast. Our study yields the first comprehensive analysis of apoptosome assembly and provides insights into complex assembly pathways.