Anti-cross-correlation between the adjacent open and closed durations of Markovian channels
Abstract
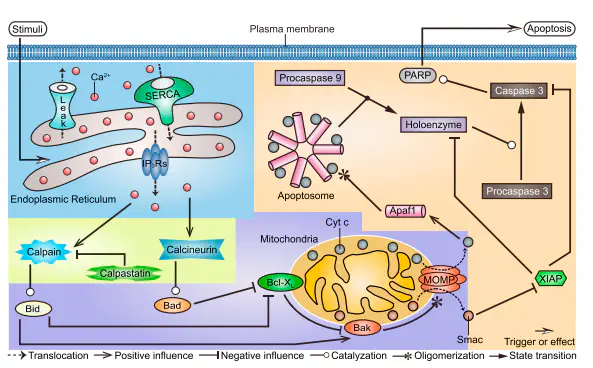
Although a rising concentration of cytosolic Ca2+ has long been recognized as an essential signal for apoptosis, the dynamical mechanisms by which Ca2+ regulates apoptosis are not clear yet. To address this, we constructed a computational model that integrates known biochemical reactions and can reproduce the dynamical behaviors of Ca2+-induced apoptosis as observed in experiments. Model analysis shows that oscillating Ca2+ signals first convert into gradual signals and eventually transform into a switch-like apoptotic response. Via the two processes, the apoptotic signaling pathway filters the frequency of Ca2+ oscillations effectively but instead responds acutely to their amplitude. Collectively, our results suggest that Ca2+ regulates apoptosis mainly via oscillation amplitude, rather than frequency, modulation. This study not only provides a comprehensive understanding of how oscillatory Ca2+ dynamically regulates the complex apoptotic signaling network but also presents a typical example of how Ca2+ controls cellular responses through amplitude modulation.