Calcium Domains around Single and Clustered IP3 Receptors and Their Modulation by Buffers
Abstract
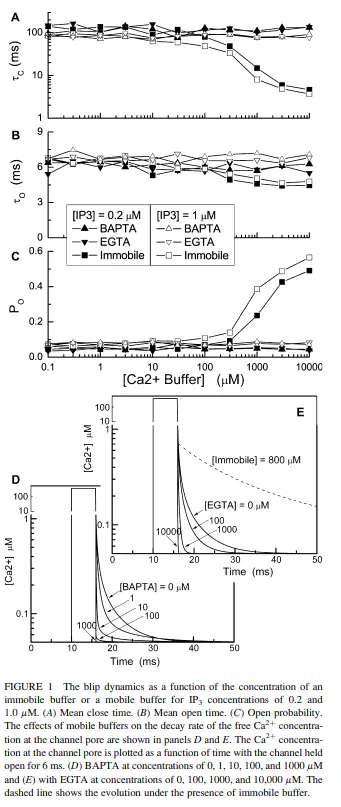
We study Ca(2+) release through single and clustered IP(3) receptor channels on the ER membrane under presence of buffer proteins. Our computational scheme couples reaction-diffusion equations and a Markovian channel model and allows our investigating the effects of buffer proteins on local calcium concentrations and channel gating. We find transient and stationary elevations of calcium concentrations around active channels and show how they determine release amplitude. Transient calcium domains occur after closing of isolated channels and constitute an important part of the channel’s feedback. They cause repeated openings (bursts) and mediate increased release due to Ca(2+) buffering by immobile proteins. Stationary domains occur during prolonged activity of clustered channels, where the spatial proximity of IP(3)Rs produces a distinct [Ca(2+)] scale (0.5-10 microM), which is smaller than channel pore concentrations (>100 microM) but larger than transient levels. While immobile buffer affects transient levels only, mobile buffers in general reduce both transient and stationary domains, giving rise to Ca(2+) evacuation and biphasic modulation of release amplitude. Our findings explain recent experiments in oocytes and provide a general framework for the understanding of calcium signals.