Revolutionizing Infection Risk Scoring: An Ensemble “From Weak to Strong” Deduction Strategy and Enhanced Point-of-Care Testing Tools
Abstract
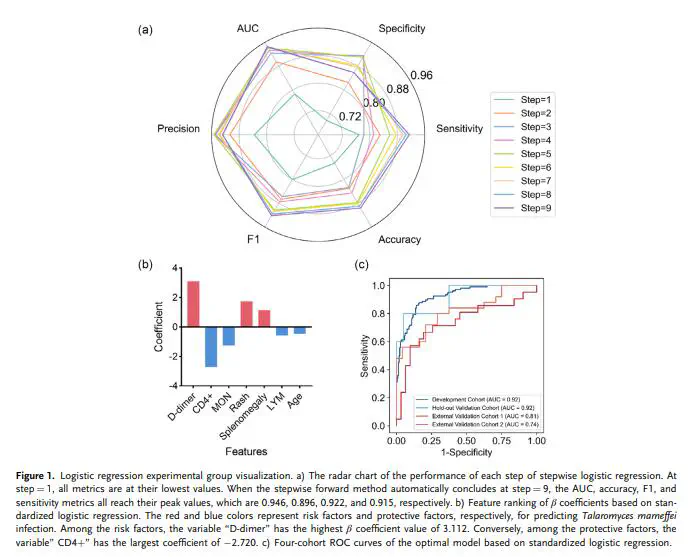
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbates challenges faced by human immunodeficiency virus patients, who are at heightened risk for infection due to compromised immune systems. This study aims to develop a reliable, home-based point-of-care testing (POCT) tool for early screening of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) coinfected with Talaromyces marneffei infection. Employing a “From weak to strong” deduction strategy for feature selection, data from 464 AIDS patients across four cohorts between February 5th, 2014, and January 8th, 2022, are analyzed. The top three features consistently observed are D-dimer, cluster of differentiation 4+, and aspartate transaminase. Based on these features, the simplest risk-scoring model is constructed, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.91, 0.80, and 0.69 in the hold-out cohort, external cohort 1, and external cohort 2, respectively. This “From weak to strong” deduction strategy identifies advantageous clinical features, enabling the development of simplified clinical risk scores with multiple biomarkers. To facilitate practical implementation, enhanced POCT tools are introduced, specifically a strip with segmented testing capabilities that demonstrates sensitivity and strong correlation with clinical scoring models. Furthermore, an open-access website and a free Android mobile app are created to support community utilization. The findings underscore the effectiveness of the innovative deduction strategy and enhanced test strips, which enable bedside measurements without laboratory dependency.